
The human papilloma virus (HPV) is the general name of a virus group that cause various diseases.More than 100 types are known.Pathogen is common worldwide.To avoid infection, it is important to know how human papillomavirus is transmitted.
What is HPV infection?
HPV infection is a group of viral diseases caused by the papillom virus.For the moment, it is studied and described above 100 types of virus.Scientists have been studying the pathogen for a long time, which has made it possible to determine what types of viruses that pathologies cause.In addition, an HPV group with a high risk of ONCO has been allocated.
Due to the fact that HPV is mainly impressed by the sexual system, gynecologists pay considerable attention to the study of the problem.Speaking of what HPV is in gynecology, it is necessary to note a high risk of developing the oncology of the cervix.Experts have found that this virus, more precisely, the 16th and 18th types cause the development of the oncological process in the female reproductive system.
HPV - Transmission and infection paths
The papilloma virus is known for its resistance to environmental factors, so for a long time, it can maintain activity in the outside environment.This explains the capacity of the pathogen to spread.However, the transmission of the HPV airborne is not directly transmitted.Speaking of the transmission of the person's papillom virus to the person, doctors indicate the compulsory presence of direct contact with the skin and the mucous membranes of the virus carrier.
The HPV transmission paths are diverse:
- sexual;
- Contact-household;
- vertical.
The most common way to transmit HPV
After hearing about this type of pathogen, patients are often interested in the doctor: if the human papillomavirus is sexually transmitted.Doctors note that this method is the most common.According to statistics, around 70% of people leading an active sex life are carriers of the papillom virus.In this case, an infection can occur several times throughout life.
Most women and men are infected with HPV already several months after the start of active sexual activity.It should be noted that often HPV is attributed to sexually transmitted infections, but infection is possible with sex without penetration.Contact with the genitals of the virus carrier can cause an infection.
Doctors also call the following infection modes by HPV:
- with a kiss;
- With oral sex.
HPV - Infection methods in daily life
Some specialists in infectious diseases distinguish the domestic path from the transmission of HPV.The percentage of the propagation of the virus in this way is low, but this possibility cannot be completely excluded.The virus can maintain the activity for a while, enter the pool, a bathtub, so infection is possible in common areas.
The infection in daily life occurs with kisses, the use of personal hygiene products of affected HPV.In such cases, the risk of infection increases:
- weakening immunity;
- Violation of personal hygiene rules.
The risk of HPV infection
The probability of HPV infection increases sharply with the start of sexual activity.This transmission path is considered the main one.At the same time, experts distinguish a number of factors, the presence of which increases the risk of infection several times:
- Beginning of sexual activity;
- Frequent change of sexual partners;
- negligence of contraceptive means.
In addition, it is necessary to say about the possibility of infection in childhood.In most cases, HPV is transmitted to the mother's child during childbirth.When promoted along the birth channel, an infection of the baby occurs.Children more easily tolerate the infection, he practically does not manifest it.In addition, thanks to the reception of ready -to -use antibodies, a spontaneous remedy is observed with mother milk.
How is HPV infection?
HPV infection occurs with direct contact with mucous membranes, the skin of the genitals.During sexual intercourse, microfissers and damage to mucous membranes often occur, which increases only at the risk of infection by HPV.At the same time, there are some differences in the virus transmission mechanisms in women and men.
How is human papillomavirus transmitted in men?

The probability of HPV infection in men depends directly on the number of permanent sexual partners.Frequent random intercourse increases the probability of infection several times.At the same time, man himself in most cases does not suspect the presence of an HPV virus in the body.As a result, the virus is spreading more.In 90% of sex cases, an infection of a partner occurs, which was absolutely healthy.
How is human papillomavirus transmitted to women?
The modes of infection by HPV in women do not differ from those which are characteristic of men.First of all is sexual.However, some factors increase the risk of infection in women.
Among these, gynecologists identify:
- Beginning of sexual activity;
- Frequent change of sexual partners;
- abortion;
- traumatic birth story;
- gynecological diseases;
- Stress;
- Long -term reception of oral contraceptives.
Is human papillomavirus transmitted to the child?
Knowing the presence of HPV in the body, women who predict a pregnancy in the near future wonder if the human papillomavirus of the mother is transmitted to the baby.Experts say that the risk of child infection exists.However, in children, HPV is rarely observed, infection methods differ from those in adults.The transmission of infection is more often at the stage of fetal advancement along the birth channel: the mother's mucosa virus passes to the baby.
It should be noted that the danger of such an infection is low.In most cases, the baby's body manages to get rid of HPV during the first 2-3 months of life.This occurs thanks to the contribution of antibodies against the nourished body with breast milk.The main danger of HPV for babies is to damage the airways - the occurrence of polyps.These cases are rare and are considered exceptions.
HPV - How much does it appear after infection?
After learning how the human papillomavirus is transmitted, many patients are interested in the terms of manifestation of the first symptoms.Doctors cannot say unequivocally how fast it manifests after the HPV infection.
The following factors are determined:
- the age of the patient;
- the presence of chronic inflammatory processes in the body;
- The state of the immune system.
In practice, the terms of the clinical manifestation of HPV are different.The appearance of a condy, changes in affected cells can be observed both after several weeks and after months.In some cases, the first lesions on the skin of the groin and genitals are a year after the papillom virus entered the body.It is possible to determine the exact time of HPV in the body based on laboratory tests.
HPV infection signs
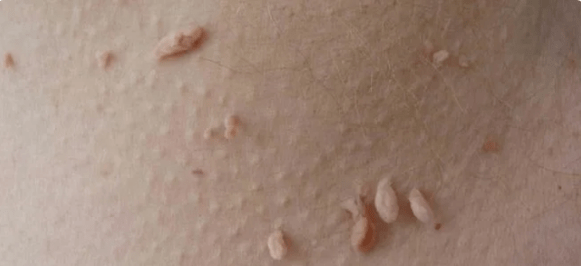
Symptoms of HPV infection are manifested by the lesion of the genitals.In most cases, the virus leads to characteristic skin lesions.Patients record the appearance of vulgar papillomas and sharp warts.Externally, these growths resemble cauliflower, so it is difficult to confuse them with other skin manifestations.
In women, pale pale pale pink growth are located:
- in the small lips;
- in the groin;
- on the clitoris;
- near the external hole of the urethra;
- On the eve of the vagina.
In some cases, condylomas are formed in the anus if a woman practices anal sex.Strong growth in these formations leads to the appearance of bloody beginnings, feelings of pain during sexual intercourse.In men, these training courses are located in the pubis region, perineum, less often on the surface of the penis.
HPV vaccinations after infection
Even those who know how human papillomavirus is transmitted, they are not always able to avoid infection.After treatment, in order to eliminate re-infection of HPV, to prevent the development of relapses, doctors are vaccinated against the papillom virus.Vaccinations prevent the development of viral infection for 15 years or more.















